How Do Producers And Consumers React Differently To Prices?
The Market. How Producers And Consumers React To Price Incentives.
Keywords searched by users: How do producers and consumers react differently to prices how does the market demand curve reflect the law of demand
What Is The Way Consumers React To A Change In Price?
Understanding Consumer Response to Price Changes
Elasticity of Demand is a crucial concept that helps us gauge how consumers respond when prices change. It quantifies the degree to which consumers adjust their purchasing behavior in response to alterations in price. In simpler terms, it tells us whether consumers are likely to keep buying a product even if its price goes up (inelastic demand) or if they are quite sensitive to price changes and may buy more or less based on those fluctuations (elastic demand).
For instance, when the demand for a product is inelastic, it implies that consumers are relatively insensitive to price changes; they will continue to purchase the product even if its price increases. Conversely, when demand is elastic, consumers are highly responsive to price adjustments, and even small changes in price can lead to significant shifts in their purchasing decisions. This understanding of elasticity of demand is essential for businesses and policymakers alike, as it helps predict and strategize for market changes and consumer behavior.
How Does Price Affect Consumers?
The impact of pricing on consumers is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. Price has a profound effect on how consumers perceive the value of a product or service, which in turn influences their purchasing decisions. It plays a pivotal role in determining whether a product or service is perceived as a good value proposition in comparison to its cost. Understanding how price influences consumer behavior involves considering factors such as affordability, quality expectations, brand reputation, and the individual’s personal financial situation. By exploring these aspects, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how price affects consumers and their choices in the marketplace.
How Do Changes In Price Affect Consumers And Producers?
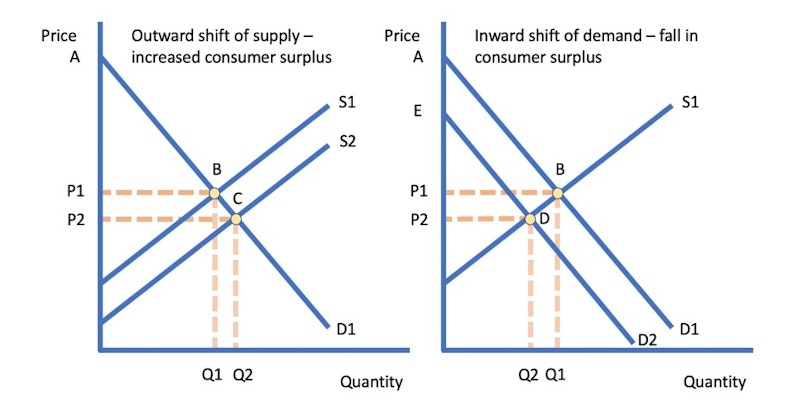
How do changes in price impact both consumers and producers? The relationship between price and production is such that as prices rise, suppliers are incentivized to increase their production to meet the heightened demand. On the other hand, as prices fall, consumers are more inclined to buy larger quantities of a product. This phenomenon is illustrated by the demand curve, which outlines the quantities consumers are willing to purchase at various price points. In essence, it reflects the fundamental dynamic between price changes, consumer behavior, and producer responses in the market.
Share 12 How do producers and consumers react differently to prices




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/supply.asp-final-f2f3f46934c64134aca94d4d528be334.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/theory-of-price.asp-Final-24772f8216aa42a6b02a1ca42f8b84da.jpg)
Categories: Top 27 How Do Producers And Consumers React Differently To Prices
See more here: b1.brokengroundgame.com

The relationship for the consumer is an inverse one: when prices are high consumers buy less, and when prices are low consumers buy more. The same cannot be said for producers. When prices are high they will bring more to the market, and when prices are low they will bring less to the market.Elasticity of Demand is a measure of how consumers react to a change in prices. Demand for a good that consumers will continue to buy despite a price increase is inelastic. Demand for a good that is very sensitive to changes in price is elastic.Pricing affects the perception of a product or service and plays a role in determining whether a product or service is worth as much as it is priced.
Learn more about the topic How do producers and consumers react differently to prices.
- 2.6: Prices as Signals – K12 LibreTexts
- Chapter 1 – What is Economics
- Use pricing to influence buyer behaviour | Onsight
- Supply and Demand: Why Markets Tick – International Monetary Fund
- How to respond to changes in your business market – NIBusinessInfo
- Effects of Prices on Producers and Consumers
See more: https://b1.brokengroundgame.com/media/

