How Does Government Intervention Lead To Market Failure: Exploring The Impact
3.4 – Market Failure (Government Intervention)
Keywords searched by users: How does government intervention cause market failure examples of failed government intervention, Market failure, What is market failure, how government intervene in market failure, market failure and government intervention pdf, Market failure example, government failure occurs when the benefits of regulation are, Government failure
Is Government Intervention A Source Of Market Failure?
Can government intervention contribute to market failure? Market failures occur when certain factors disrupt the smooth functioning of markets, such as when polluters avoid paying for the environmental damage they cause. However, it’s important to note that these market failures, also referred to as “distortions,” can stem from actions taken by the government itself. In some cases, government policies, regulations, or interventions can unintentionally create inefficiencies or imbalances in the market, leading to undesirable economic outcomes. This raises the question of whether government intervention, while intended to address issues, can sometimes inadvertently contribute to market failures.
What Is Market Failure And The Case For Government Intervention?
Market failure refers to situations in which the free market, left to its own devices, fails to allocate resources efficiently, leading to undesirable outcomes for society. In such cases, government intervention becomes essential to rectify these market deficiencies and promote overall well-being.
There are several key types of market failures that warrant government intervention:
-
Asymmetric Information: This occurs when one party in a transaction has more information than the other, leading to adverse selection and moral hazard. Government intervention, such as regulations requiring disclosure or consumer protection laws, can help mitigate these issues.
-
Concentrated Market Power: When a few firms dominate an industry, they can engage in anti-competitive behavior, such as price-fixing or monopolistic practices, which harm consumers. Government intervention through antitrust laws and regulatory oversight aims to maintain competition and prevent abuse of market power.
-
Public Goods: These are goods or services that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning that it is difficult to exclude anyone from using them, and one person’s use doesn’t diminish their availability to others. Government provision is often necessary for public goods like national defense, as the private sector may underproduce them due to the inability to charge users directly.
-
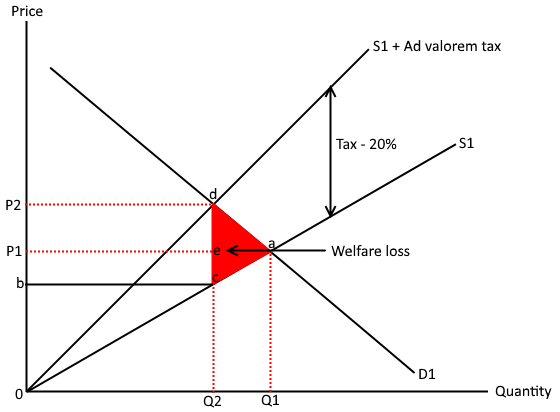
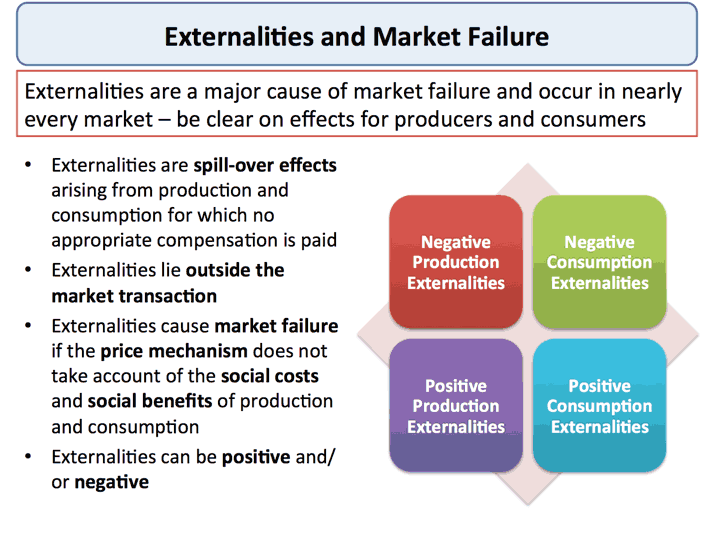
Externalities: Externalities are unintended side effects of economic activities that affect third parties who are not part of the transaction. For instance, pollution is a negative externality that can harm the environment and public health. Government intervention, such as emissions regulations or taxes, can internalize these external costs and promote socially optimal outcomes.
In summary, market failures can stem from information imbalances, monopolistic practices, public goods, or externalities, and they often necessitate government intervention to safeguard the interests of society as a whole. Recognizing and addressing these market failures is crucial for promoting a fair and efficient economy that benefits everyone. [Date added: September 14, 2023]
Discover 42 How does government intervention cause market failure





Categories: Discover 11 How Does Government Intervention Cause Market Failure
See more here: b1.brokengroundgame.com

Learn more about the topic How does government intervention cause market failure.
- Market Failures, Public Goods, and Externalities – Econlib
- Defining Market Failure (with Examples) – EdChoice
- Examples of how government intervention can cause …
- Government Intervention & Failure – A Level Economics B …
- Government Failure: Definition & Examples
- MARKET FAILURE AND GOVERNMENT INTERVENTION
See more: https://b1.brokengroundgame.com/media/

