What Happens To Glycogen If Not Used: Unraveling Its Fate
What Is Glycogen? – Dr. Berg
Keywords searched by users: What happens to glycogen if not used if carbohydrates are not used for energy what happens to them, what happens to excess carbohydrates in the body, what parts of the body use glucose for energy?, Glycogen structure, What is carb, How insulin works, Gluconeogenesis, What is starch
What Happens If You Don’T Use Glycogen?
On the other hand, when your body’s muscle glycogen stores become depleted, it can lead to fatigue. Muscle glycogen plays a crucial role in providing energy during physical activity. When these glycogen stores are running low, the muscle cells cannot produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) quickly enough to sustain the intensity of exercise. ATP is the primary energy currency in our cells, and its shortage during physical exertion results in the sensation of fatigue. This depletion of muscle glycogen and its impact on ATP production and fatigue were observed in a study conducted on February 10, 2018, further underscoring its significance in understanding exercise physiology.
What Happens To Unused Glucose?
What happens to unused glucose? When your body has consumed the necessary energy for its immediate needs, any surplus glucose is carefully stored in compact packages known as glycogen, primarily within the liver and muscles. This glycogen storage serves as a readily accessible energy reserve, capable of sustaining your body for approximately a day without additional food intake. However, as time passes without eating, your blood glucose levels gradually decrease. This natural process ensures that your body maintains a stable supply of energy to meet its demands. Please note that the date mentioned, August 3, 2022, is not relevant to the explanation and can be omitted.
Does Unused Glycogen Turn Into Fat?
Is Unused Glycogen Converted into Fat?
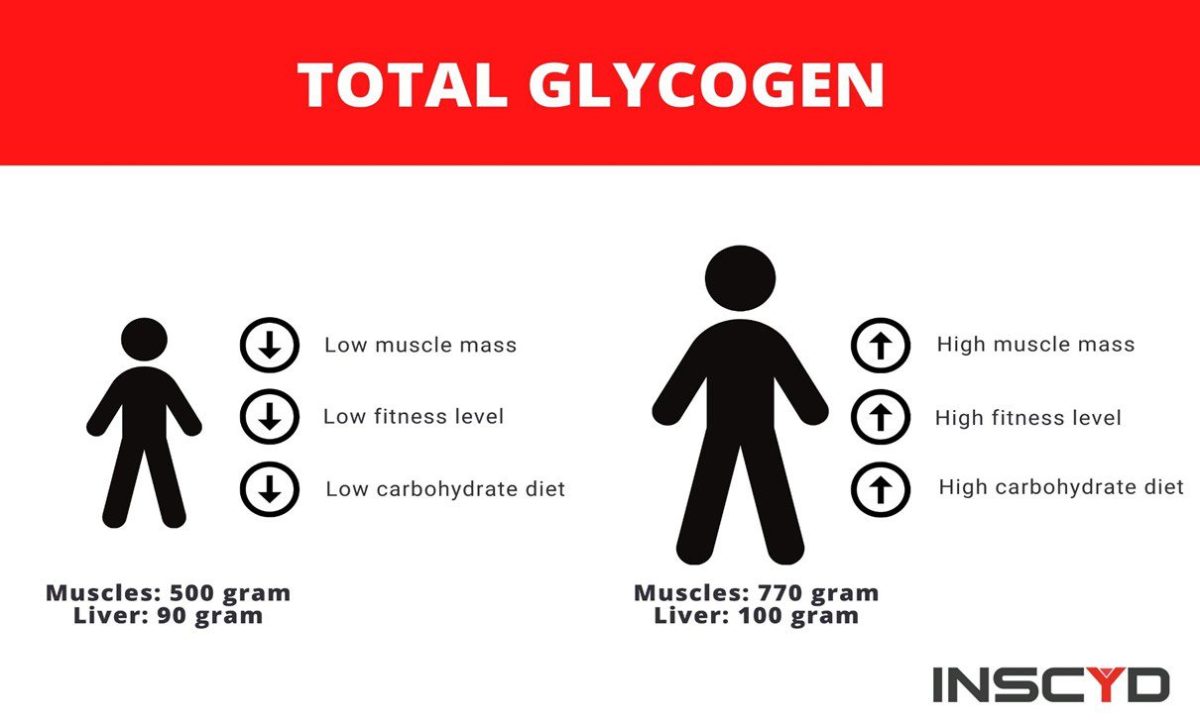
Glycogen, a storage form of glucose, can be stored in the human body to a capacity of approximately 600 grams. Beyond this limit, any surplus glycogen undergoes a transformation into triglycerides, a type of fat. These triglycerides serve a dual purpose; they can either be utilized as an energy source directly by entering the bloodstream, or they may be stored in the body’s fat reserves for future use. This process plays a significant role in maintaining energy balance and metabolic functions.
Share 20 What happens to glycogen if not used






Categories: Aggregate 37 What Happens To Glycogen If Not Used
See more here: b1.brokengroundgame.com

Excess glycogen is stored in the liver where it may be used later for energy. Your muscles are also a storage area for glycogen. Excess glucose above this can be converted into triglycerides which are stored in your fat cells.Conversely, the depletion of muscle glycogen causes fatigue. When muscle glycogen stores are low, muscle cells cannot produce ATP rapidly enough to maintain exercise intensity,73 the very definition of fatigue.After your body has used the energy it needs, the leftover glucose is stored in little bundles called glycogen in the liver and muscles. Your body can store enough to fuel you for about a day. After you haven’t eaten for a few hours, your blood glucose level drops.
Learn more about the topic What happens to glycogen if not used.
- The Role of Glycogen in Diet and Exercise – Verywell Fit
- Fundamentals of glycogen metabolism for coaches and athletes
- What Is Glucose? – WebMD
- Burning Fat Vs. Glycogen – Livestrong.com
- Glycogen Storage Disease (GSD) – Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
- Physiology, Fasting – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
See more: https://b1.brokengroundgame.com/media/

