What Is A Positive Externality: Uncovering The Hidden Benefits
Positive And Negative Externalities Defined \U0026 Explained In One Minute: Education Vs. Pollution?
Keywords searched by users: What is a positive externality Negative externality, Positive externality examples, Positive consumption externality example, Negative externality examples, Negative production externality, A negative externality generates, Example of negative consumption externality, An externality is defined as
What Is A Positive Externality Example?
A positive externality is a situation where the production or consumption of a product results in additional benefits for individuals or society as a whole beyond what is directly intended or paid for. This concept is essential in economics to understand how certain activities can create positive spillover effects. To illustrate, let’s consider education as a classic example of a positive externality. When individuals attend school and receive an education, they not only acquire knowledge and skills for their personal and professional development but also contribute to the overall betterment of society. This is because an educated population can lead to increased productivity, innovation, and a higher standard of living for everyone.
In contrast, negative externalities represent the opposite scenario, where the production or consumption of a product imposes additional costs on individuals or society, often without those responsible for the negative effects having to bear the full burden of those costs. An example of a negative externality could be pollution from a factory that harms the environment and the health of nearby residents, leading to increased healthcare expenses and a diminished quality of life for affected individuals.
It’s important to note that positive and negative externalities have significant implications for policy decisions, as governments and policymakers often intervene to address externalities, either by encouraging activities with positive externalities (like subsidizing education) or by regulating or taxing activities with negative externalities (such as imposing pollution controls on factories). This understanding of externalities helps us make more informed choices to promote societal well-being while minimizing unintended consequences. Please note that the date “10th March 2023” in the original passage appears to be unrelated and has been omitted in this revised explanation.
What Is A Positive Externality Simple Definition?
A positive externality, in simple terms, refers to a situation where an additional benefit extends beyond the primary parties involved in a transaction. In other words, it occurs when some of the favorable outcomes of an economic exchange benefit individuals or groups other than the producer or consumer directly participating in that exchange. To put it more clearly, positive externalities highlight instances where positive effects “spill over” to parties not directly engaged in the transaction, resulting in broader societal gains beyond the immediate participants.
What Are 3 Examples Of Positive Externalities?
Positive externalities are situations where the benefits of an activity or choice extend beyond the individual engaging in that activity. Here are three examples to illustrate this concept:
-
Good Architecture: When someone invests in creating a beautifully designed and well-maintained building, it not only enhances their own property but also adds aesthetic value to the surrounding neighborhood. People who pass by or live nearby experience improved visual surroundings, contributing to a more pleasant and attractive community.
-
Buying Flowers for a Front Garden: Planting flowers in a front garden not only brings joy to the homeowner but also offers a delightful sight for those who walk past the house. The visual appeal of the garden uplifts the spirits of pedestrians, making the neighborhood a more enjoyable place to live and visit.
-
Consuming a Healthy Diet: Opting for a nutritious diet not only benefits the individual’s health but also has positive externalities for society as a whole. A population that practices healthy eating habits tends to have lower healthcare costs due to reduced instances of chronic diseases. Additionally, individuals who eat well often exhibit higher productivity and contribute positively to the workforce, thereby boosting the overall economic well-being of the community.
-
Education and Learning New Skills: When individuals pursue education and acquire new skills, they not only improve their own prospects but also contribute to the broader society. Educated and skilled individuals are more likely to engage in productive work, innovate, and positively influence the economy. Moreover, a well-educated populace fosters a culture of knowledge-sharing, which can lead to further advancements and improvements in society.
In summary, positive externalities highlight how certain choices and actions can generate benefits that extend beyond the individual, enriching the lives and well-being of others in the community.
Details 31 What is a positive externality




Categories: Aggregate 71 What Is A Positive Externality
See more here: b1.brokengroundgame.com

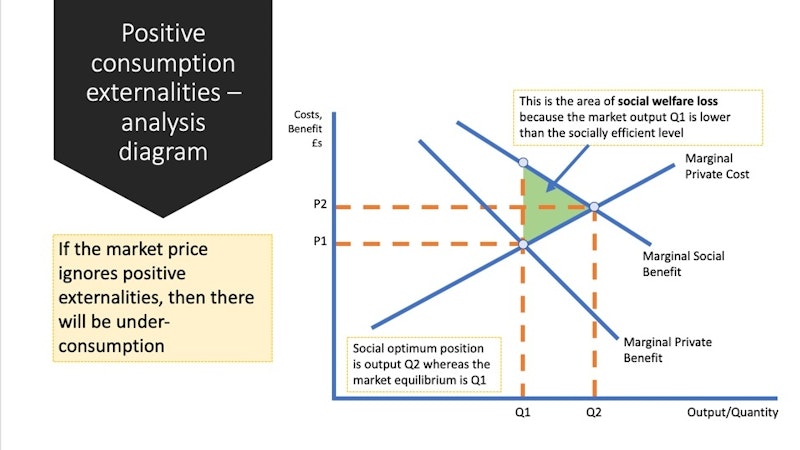
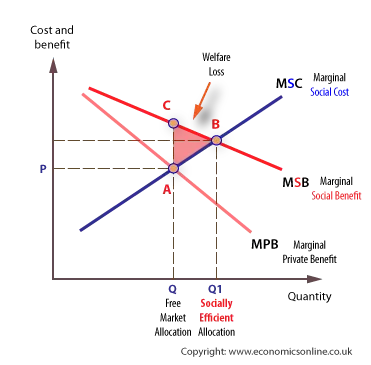
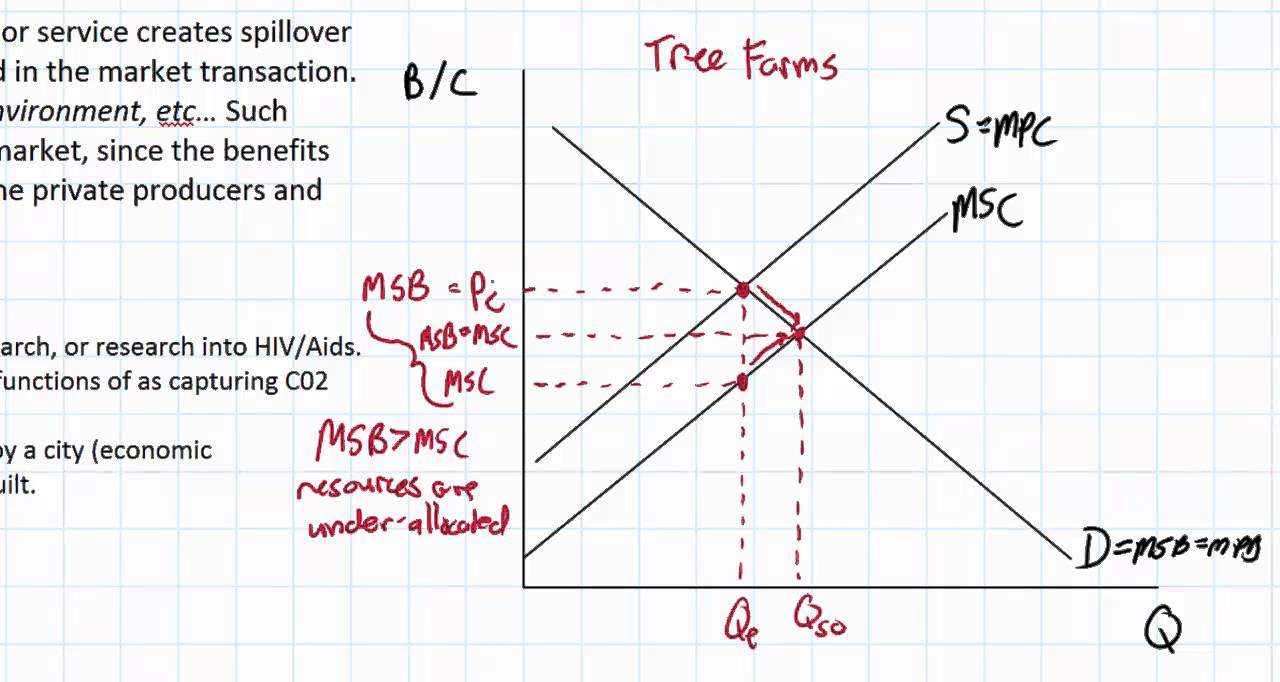
A positive externality exists if the production and consumption of a good or service benefits a third party not directly involved in the market transaction.A positive externality is a benefit of producing or consuming a product. For example, education is a positive externality of school because people learn and develop skills for careers and their lives. In comparison, negative externalities are a cost of production or consumption.A positive externality occurs when a benefit spills over. So, externalities occur when some of the costs or benefits of a transaction fall on someone other than the producer or the consumer.
- Good architecture. …
- Buying flowers for front garden gives benefits to others who walk past.
- Consuming a healthy diet ultimately will benefit others in society because less health care costs, higher productivity.
- Education or learning new skills.
Learn more about the topic What is a positive externality.
- Positive externality | economics – Britannica
- Positive and Negative Externality: Definition and Examples
- Externalities, Economic Lowdown Podcasts | Education
- Positive Externalities – Economics Help
- Positive Externalities Flashcards – Quizlet
- What are public goods? (article) | Khan Academy
See more: https://b1.brokengroundgame.com/media/

