What Is An Example Of Genomics: Illuminating The Power Of Genetic Sequencing
What Is Genomics – Full Length
Keywords searched by users: What Is An Example Of Genomics What is genomics, importance of genomics, genomics topics for presentation, what is genome in biology, genome example biology, Introduction to genomics, Genomics, genomics uses
What Are The Two Types Of Genomics?
Genomics can be broadly categorized into two main types: structural genomics and functional genomics. Structural genomics focuses on deciphering the three-dimensional structures of all the proteins encoded by an organism’s genome. This type of genomics provides valuable insights into the physical architecture of proteins, which is essential for understanding their functions and interactions within the cell.
On the other hand, functional genomics is primarily concerned with gathering and utilizing data obtained through sequencing techniques to describe the functions of genes and proteins. It delves into how genes are expressed, regulated, and how their products, such as proteins, contribute to various biological processes. By exploring both the form (structural genomics) and function (functional genomics) of genetic elements, researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of the genetic underpinnings of life and the mechanisms governing cellular processes. These two branches of genomics complement each other, providing a holistic view of the genetic and molecular landscapes that drive living organisms.
What Is Genomics Used For?
Genomics serves as a comprehensive field dedicated to exploring the entirety of an organism’s genetic material, commonly referred to as the genome. To accomplish this, genomics employs a combination of advanced computational methods and mathematical techniques known as bioinformatics. These tools allow genomics researchers to sift through vast volumes of DNA sequence data, enabling them to pinpoint genetic variations that have significant implications for health, disease susceptibility, or individual responses to pharmaceuticals. In essence, genomics plays a pivotal role in unraveling the intricate genetic makeup of organisms, providing valuable insights into various facets of biology and medicine.
What Are Four Types Of Genomics?
Exploring Various Genomic Testing Approaches
Genomics encompasses a diverse range of testing methodologies, each serving distinct purposes in the realm of healthcare and research. Here, we delve into four prominent types of genomic testing, shedding light on their unique functions:
-
Diagnostic Testing: This type of testing primarily aims to provide a clear-cut yes or no answer. It plays a pivotal role in identifying the presence or absence of specific genetic mutations or conditions, aiding in disease diagnosis and prognosis.
-
Clinical Predictive Testing: This form of genomics focuses on forecasting an individual’s susceptibility to certain diseases or conditions based on their genetic makeup. It helps healthcare professionals tailor preventive measures and personalized treatments.
-
Pharmacogenomic Testing: Pharmacogenomics examines how an individual’s genetic profile influences their response to medications. This vital information assists healthcare providers in prescribing the most effective and safe drugs, minimizing adverse reactions.
-
Tumor Testing: In the realm of oncology, tumor testing is indispensable. It involves scrutinizing the genetic alterations within cancer cells to guide treatment decisions. By understanding the genetic drivers of a tumor, healthcare teams can develop targeted therapies for more successful outcomes.
In summary, these four types of genomic testing encompass diagnostic precision, predictive insights, personalized medicine, and tailored cancer treatments, collectively advancing the field of genomics to benefit patients and researchers alike. [Date: September 13, 2023]
Aggregate 25 What Is An Example Of Genomics




Categories: Collect 72 What Is An Example Of Genomics
See more here: b1.brokengroundgame.com
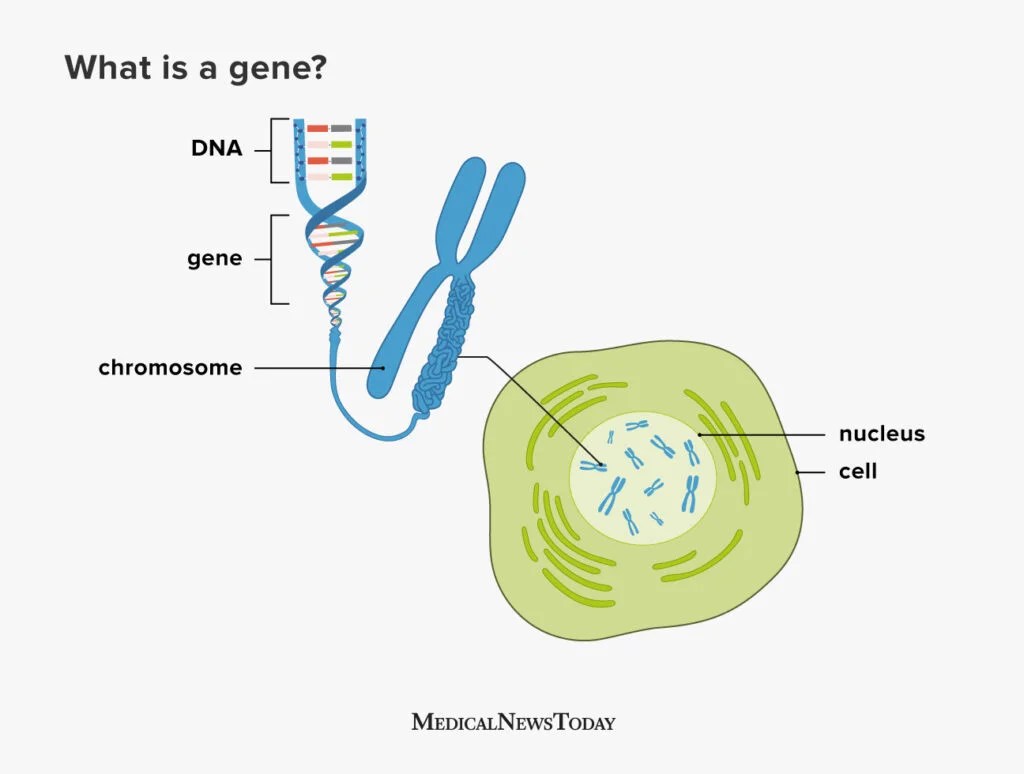
Genomics includes the scientific study of complex diseases such as heart disease, asthma, diabetes, and cancer because these diseases are typically caused more by a combination of genetic and environmental factors than by individual genes.Types of genomics
Structural genomics: Aims to determine the structure of every protein encoded by the genome. Functional genomics: Aims to collect and use data from sequencing for describing gene and protein functions.Genomics, in contrast, is the study of the entirety of an organism’s genes – called the genome. Using high-performance computing and math techniques known as bioinformatics, genomics researchers analyze enormous amounts of DNA-sequence data to find variations that affect health, disease or drug response.
- Diagnostic testing. A diagnostic test should usually give a yes/no result. …
- Clinical predictive testing. …
- Pharmacogenomic testing. …
- Tumour testing.
Learn more about the topic What Is An Example Of Genomics.
- Genetics vs. Genomics Fact Sheet
- What is genomics? | Definition from TechTarget
- Genetics vs. genomics – Important Distinctions – The Jackson Laboratory
- Four types of genomic testing explained
- Ranking genomic features using an information-theoretic measure of …
- Chapter 4 Genome type | PSS Online Bio School – What is a gene?
See more: https://b1.brokengroundgame.com/media/

